Paper: Infrared spectral histopathology using haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained glass slides: a major step forward towards clinical translation
 Infrared spectral histopathology using haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained glass slides: a major step forward towards clinical translation
Infrared spectral histopathology using haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained glass slides: a major step forward towards clinical translation
Michael J. Pilling, Alex Henderson, Jonathan H. Shanks, Michael D. Brown, Noel W. Clarke and Peter Gardner
Analyst 142 (2017) 1258-1268
doi: 10.1039/C6AN02224C
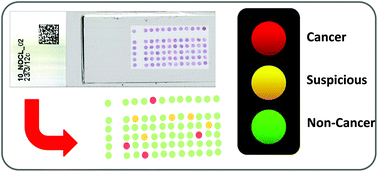 Infrared spectral histopathology has shown great promise as an important diagnostic tool, with the potential to complement current pathological methods. While promising, clinical translation has been hindered by the impracticalities of using infrared transmissive substrates which are both fragile and prohibitively very expensive. Recently, glass has been proposed as a potential replacement which, although largely opaque in the infrared, allows unrestricted access to the high wavenumber region (2500–3800 cm−1). Recent studies using unstained tissue on glass have shown that despite utilising only the amide A band, good discrimination between histological classes could be achieved, and suggest the potential of discriminating between normal and malignant tissue. However unstained tissue on glass has the potential to disrupt the pathologist workflow, since it needs to be stained following infrared chemical imaging. In light of this, we report on the very first infrared Spectral Histopathology SHP study utilising coverslipped H&E stained tissue on glass using samples as received from the pathologist. In this paper we present a rigorous study using results obtained from an extended patient sample set consisting of 182 prostate tissue cores obtained from 100 different patients, on 18 separate H&E slides. Utilising a Random Forest classification model we demonstrate that we can rapidly classify four classes of histology of an independent test set with a high degree of accuracy (>90%). We investigate different degrees of staining using nine separate prostate serial sections, and demonstrate that we discriminate on biomarkers rather than the presence of the stain. Finally, using a four-class model we show that we can discriminate normal epithelium, malignant epithelium, normal stroma and cancer associated stroma with classification accuracies over 95%.
Infrared spectral histopathology has shown great promise as an important diagnostic tool, with the potential to complement current pathological methods. While promising, clinical translation has been hindered by the impracticalities of using infrared transmissive substrates which are both fragile and prohibitively very expensive. Recently, glass has been proposed as a potential replacement which, although largely opaque in the infrared, allows unrestricted access to the high wavenumber region (2500–3800 cm−1). Recent studies using unstained tissue on glass have shown that despite utilising only the amide A band, good discrimination between histological classes could be achieved, and suggest the potential of discriminating between normal and malignant tissue. However unstained tissue on glass has the potential to disrupt the pathologist workflow, since it needs to be stained following infrared chemical imaging. In light of this, we report on the very first infrared Spectral Histopathology SHP study utilising coverslipped H&E stained tissue on glass using samples as received from the pathologist. In this paper we present a rigorous study using results obtained from an extended patient sample set consisting of 182 prostate tissue cores obtained from 100 different patients, on 18 separate H&E slides. Utilising a Random Forest classification model we demonstrate that we can rapidly classify four classes of histology of an independent test set with a high degree of accuracy (>90%). We investigate different degrees of staining using nine separate prostate serial sections, and demonstrate that we discriminate on biomarkers rather than the presence of the stain. Finally, using a four-class model we show that we can discriminate normal epithelium, malignant epithelium, normal stroma and cancer associated stroma with classification accuracies over 95%.